What is Virtual Reality

What is Virtual Reality
Discover the immersive world of Virtual Reality (VR). Learn what is Virtual Reality, how it works, its history, applications in various industries, and what the future holds for this groundbreaking technology.
Introduction to Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) is a groundbreaking technology that creates an artificial, computer-generated environment. Users can experience this immersive digital world as if they were physically present within it through VR headsets. VR has evolved significantly in recent years, becoming more accessible and influencing industries far beyond entertainment, including education, healthcare, and real estate. This article aims to provide a deep understanding of VR, how it works, and its varied applications in the modern world.
What is Virtual Reality (VR)?
- Virtual Reality (VR) is a simulated experience that mimics or transcends the real world, allowing users to immerse themselves in a computer-generated environment. Unlike conventional user interfaces, VR places the user inside an experience. Instead of viewing a screen, users can interact with 3D worlds using VR headsets, sensors, and other hardware devices. These systems allow users to look around the artificial world, move in, and manipulate virtual objects.
- At its core, VR aims to replicate the user’s physical presence in a virtual setting, making them feel as if they are part of the environment they are experiencing. This can range from simple 360-degree videos to highly interactive and realistic environments used in gaming and professional training.
How Does Virtual Reality Work?
Virtual Reality combines hardware and software to create a virtual environment that users can interact with. The hardware typically includes VR headsets, gloves, and motion controllers, which enable users to interact with their surroundings in a virtual space. Here’s how the technology functions:
- Head Tracking:
VR headsets use sensors like gyroscopes, accelerometers, and magnetometers to track the movement of your head. As you look around in the real world, the display adjusts to simulate the change in perspective in the virtual environment. - Motion Tracking:
Some advanced systems include motion-tracking features, allowing users to move around a virtual space. Sensors around the room or on the user can track their movements, translating them into the virtual world. - Display Technology:
Most VR headsets use two displays, one for each eye, which creates a stereoscopic 3D effect. Combined with a wide field of view, this tricks the brain into perceiving depth and space in the virtual world. - Haptic Feedback:
Haptic technology simulates touch, allowing users to feel sensations in the virtual world through specialized gloves, vests, or controllers that provide feedback such as vibrations or force. - Sound:
3D sound technology enhances the immersive experience by mimicking how sound behaves in real life, allowing users to hear sounds from different directions as they move in the virtual space.
History of Virtual Reality:
- The idea of Virtual Reality has been around for decades. Early attempts to create immersive environments were made as far back as the 1960s. Morton Heilig, often called the “father of Virtual Reality,” created the Sensorama, a mechanical device that simulated riding a motorcycle through a city using sights, sounds, and vibrations. This is considered one of the first steps toward VR.
- In the 1980s and 1990s, VR gained more public attention, mainly through its portrayal in science fiction films and the development of early commercial VR systems like the Sega VR and Nintendo’s Virtual Boy. However, these systems were not widely adopted due to their high costs and technical limitations.
- It wasn’t until the 2010s that VR made a significant comeback. Palmer Luckey’s company, Oculus VR, released the Oculus Rift, which became one of the first widely successful VR headsets. This success led other tech giants like Sony, Google, and HTC to invest in VR, and the technology has continued to evolve.
Critical Components of VR Systems:
A VR system consists of several essential components that work together to deliver an immersive experience:
- VR Headsets:
The most recognizable component, a VR headset, displays the virtual world in front of the user’s eyes. The headsets often include built-in sensors that track the user’s head movements to ensure the visuals match the user’s perspective. - Controllers and Gloves:
Handheld controllers and gloves allow users to interact with virtual objects. These controllers track the position of your hands and fingers, translating movements into actions within the virtual world. - Sensors:
External sensors or cameras often track a user’s body movement. Some systems are capable of full-body tracking, allowing users to walk around in the virtual environment. - Haptic Feedback Devices:
Haptic gloves or vests provide tactile feedback, simulating touch sensations in the virtual world. This can range from a simple vibration to simulate touch or more advanced sensations like pressure. - Software:
The software generates the virtual environment. Game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine are often used to develop VR applications for gaming, training simulations, or education.

Types of Virtual Reality:
There are different levels of immersion within VR, ranging from simple desktop experiences to fully immersive systems. Here are the three main types of Virtual Reality:
- Non-Immersive VR:
Non-immersive VR offers a computer-generated environment where users interact with the virtual space on a regular display. The user may use a keyboard, mouse, or joystick to control the environment. This is often seen in video games and other desktop applications. - Semi-Immersive VR:
This type of VR offers a more immersive experience than non-immersive VR but doesn’t fully envelop the user. Semi-immersive VR typically uses large screens or VR goggles but limits the user’s physical movement in the virtual world. It is often used in educational environments and flight simulators. - Fully Immersive VR:
Fully immersive VR provides the most immersive experience, where users can interact with a 3D virtual world through a VR headset, motion-tracking sensors, and sometimes haptic feedback devices. This type of VR is commonly used in gaming, training, and professional simulations.
Virtual Reality vs. Augmented Reality:
While both Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are immersive technologies, they have fundamental differences.
- Virtual Reality:
VR transports the user into a digital environment that replaces the real world. It creates an entirely new space that users can explore and interact with. - Augmented Reality (AR)
overlays digital objects onto the real world. Instead of immersing users in an entirely virtual environment, AR enhances their existing surroundings. An example of AR would be Pokémon Go, where virtual characters appear on your phone’s camera as part of the real world.
While both technologies share similarities, they serve different purposes and are used in varied industries.
Popular Devices and Platforms for VR:
- Oculus Rift:
Developed by Oculus VR (now owned by Meta), the Oculus Rift is one of the most popular VR headsets. It features high-resolution displays, precise motion tracking, and various games and applications. - HTC Vive:
The HTC Vive is known for its room-scale VR, where users can walk around and explore virtual environments. Its built-in sensors offer precise movement tracking, creating a more immersive experience. - PlayStation VR:
Sony’s PlayStation VR is a popular VR headset for console gamers. Designed for the PlayStation 4 and PlayStation 5, this headset offers a wide range of exclusive VR titles and a more affordable entry point for gamers.
VR in Gaming:
Gaming is the most recognized application of Virtual Reality. VR has transformed the gaming industry, offering players unprecedented immersion. Instead of controlling a character on a screen, players can physically interact with the game’s world. Some popular VR games include:
- Beat Saber:
A rhythm-based game where players slash through blocks to the beat of the music. - Half-Life: Alyx:
A critically acclaimed first-person shooter that fully exploits VR’s capabilities. - The Walking Dead: Saints & Sinners:
A survival horror game that immerses players in the post-apocalyptic world of The Walking Dead.
VR gaming continues to evolve, with developers experimenting with new ways to merge Reality and digital worlds.

VR in Education:
Virtual Reality has made its mark in education by providing immersive learning experiences. With VR, students can:
- Take virtual field trips to historical landmarks or outer space.
- Explore the human body through interactive anatomy lessons.
- Conduct chemistry experiments in virtual labs without the risk of harmful substances.
VR allows educators to break the limitations of traditional teaching methods, providing students with hands-on learning in an engaging, interactive way.

VR in Healthcare:
Healthcare is another field where VR has proven transformative. VR has a wide range of medical applications, from training doctors to treating patients. Some of these include:
- Medical Training:
VR simulations allow medical professionals to practice surgeries or procedures in a risk-free environment, helping them refine their skills before performing on actual patients. - Therapy for PTSD and Anxiety:
VR is used in exposure therapy to treat conditions like PTSD, anxiety, and phobias. Patients can confront their fears in a controlled environment, helping them to overcome trauma. - Physical Rehabilitation:
Patients recovering from injuries can use VR-based physical therapy exercises, making rehabilitation more engaging and motivating.
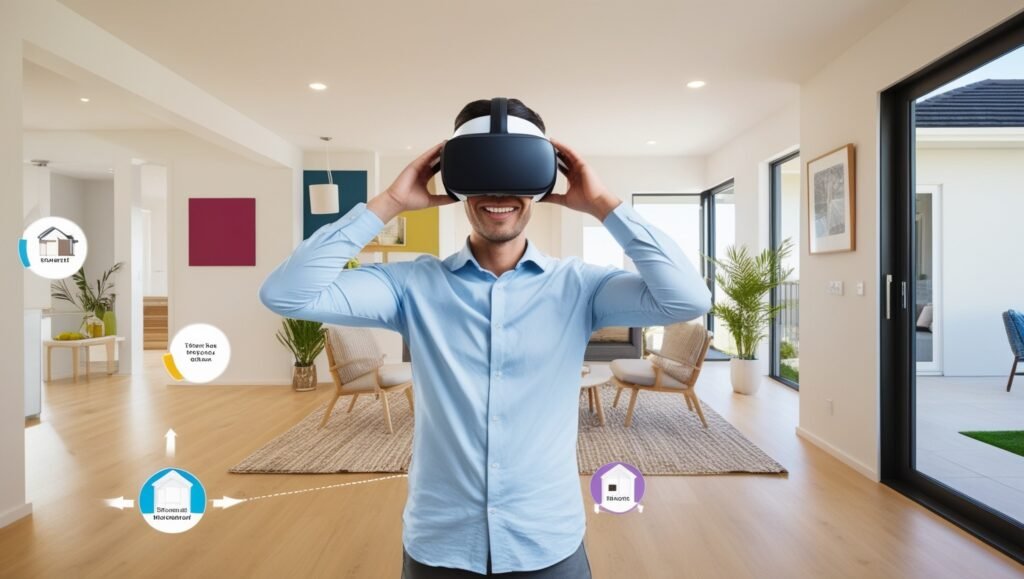
VR in Real Estate:
The real estate industry has adopted VR as a way to offer virtual tours of properties. This technology allows potential buyers to walk through a house or apartment without being physically present. Some advantages of VR in real estate include:
- Time-Saving:
Buyers can view multiple properties quickly without traveling from one location to another. - Broader Reach:
International buyers can view properties worldwide, giving real estate agents access to a global market. - Customization:
VR tools allow users to change the color of walls, furniture, or layouts to visualize how the property could look after renovation.

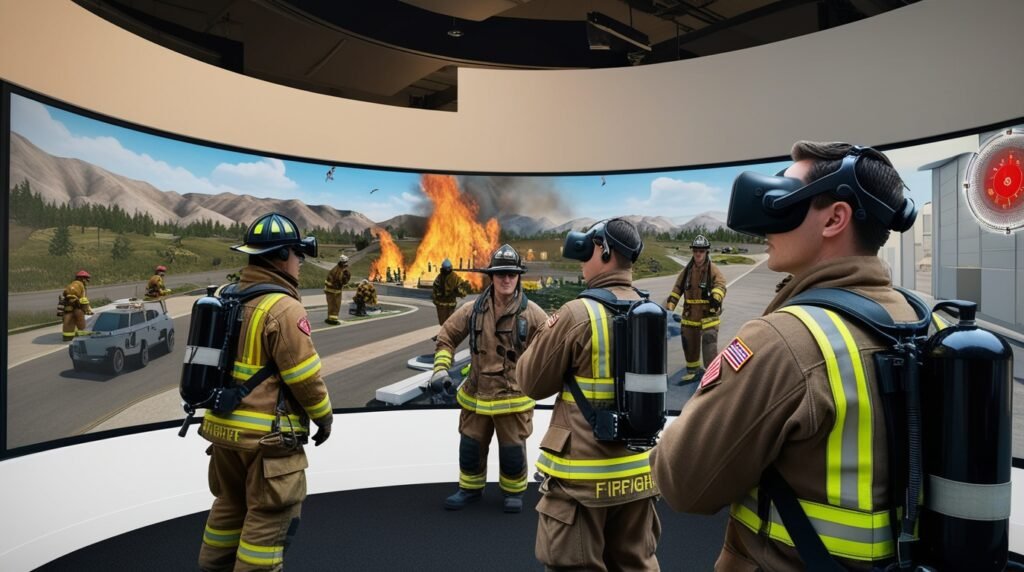
VR in Training and Simulation:
Industries like aviation, defense, and emergency services use VR for training and simulations. These environments provide a safe space for professionals to practice complex and dangerous tasks. Examples include:
- Flight Simulators:
Pilots use VR to practice flying aircraft in different weather conditions or emergency scenarios. - Military Training:
Soldiers use VR for combat training simulations, helping them prepare for various missions and situations. - Customer Service Training:
VR simulates customer interactions, allowing employees to practice responding to difficult situations in a controlled environment.

Benefits of Virtual Reality:
The advantages of VR extend beyond entertainment. Here are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Learning and Training:
VR offers hands-on experiences that help learners and professionals master complex skills in a safe environment. - Immersive Entertainment:
VR provides gamers and movie enthusiasts with an unmatched level of immersion, making experiences more interactive and realistic. - Therapeutic Applications:
VR has proven effective in treating mental health conditions like PTSD, anxiety, and phobias. - Business Solutions:
VR allows companies to offer virtual tours, simulations, and interactive marketing experiences, improving customer engagement and decision-making.
Limitations and Challenges of Virtual Reality:
While VR offers many benefits, it also has its limitations:
- High Costs:
High-quality VR systems can be expensive, limiting their accessibility for consumers and businesses. - Motion Sickness:
Some users experience motion sickness while using VR, particularly in systems that don’t synchronize well with the user’s movements. - Technical Limitations:
Despite advancements, VR systems still face limitations regarding resolution, field of view, and motion tracking accuracy. - Ethical Concerns:
VR raises ethical questions regarding privacy, addiction, and the potential psychological effects of long-term use.
The Future of Virtual Reality:
The future of Virtual Reality is promising, with continuous advancements in hardware and software. Areas of growth include:
- Improved Accessibility:
Lower prices and more user-friendly systems will make VR accessible to a broader audience. - Social VR:
Companies like Meta (formerly Facebook) are developing social platforms where users can meet, interact, and socialize in virtual environments. - Enhanced VR in Education:
Virtual classrooms will become more immersive, enabling students to learn in environments tailored to their needs. - More Realistic Interactions:
Improvements in graphics, artificial intelligence, and motion tracking will create even more lifelike and interactive VR experiences.
Ethical Considerations of VR:
As VR continues to evolve, ethical concerns arise, particularly around:
- Privacy:
As VR systems collect vast amounts of user data, including their movements and interactions, safeguarding user privacy is critical. - Addiction:
Some users may become overly reliant on VR for entertainment or social interaction, leading to potential addiction. - Psychological Effects:
Long-term exposure to highly immersive VR environments may blur the line between Reality and the virtual world, causing disorientation or other mental health issues.
How to Get Started with VR:
Getting started with VR is easier than ever. Here’s what you need:
- Choose a VR Headset:
Entry-level options like the Oculus Quest 2 are affordable and don’t require a high-end PC. More advanced systems like the HTC Vive or PlayStation VR offer a richer experience but come at a higher price. - Select a Platform:
Most VR headsets are compatible with platforms like SteamVR, Oculus Store, or PlayStation Network, where you can find VR games and applications. - Find Your Space:
Ensure you have enough physical space to move around while using your VR system. Some systems, like the HTC Vive, require room-scale movement, while others are more stationary.
Emerging Trends in Virtual Reality:
- Social VR Platforms:
Platforms like VR Chat and Horizon Worlds (by Meta) allow users to meet, socialize, and interact in virtual environments, paving the way for virtual communities. - VR for Remote Work:
Virtual office spaces are emerging for teams to collaborate in VR, simulating in-person meetings without geographical limitations. - Fitness in VR:
VR is also making waves in the fitness industry. Gamified workout apps like Supernatural and FitXR allow users to engage in immersive exercise routines.
Companies Leading the VR Revolution:
- Meta (Facebook):
Meta, through its Oculus VR division, is investing heavily in VR for social networking and business applications. - Google:
Google has experimented with VR through products like Google Cardboard and Daydream View, though it is now focusing on VR software development. - Sony:
Sony’s PlayStation VR is a leader in the gaming industry, offering an extensive library of immersive VR titles. - HTC:
HTC’s Vive platform is known for its high-quality, room-scale VR experiences, which are popular in gaming and professional applications. - Microsoft:
Microsoft is focusing on Mixed Reality (MR) and Augmented Reality (AR) through its HoloLens, but it also plays a role in VR development for enterprise solutions.

Conclusion:
Virtual Reality has proven to be a transformative technology, offering users immersive experiences in entertainment, education, healthcare, and beyond. Technology will become even more integrated into daily life, offering new ways to learn, work, and play. The future of VR is bright, and it will undoubtedly continue to reshape how we experience the world around us.
FAQs
- What is the difference between Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality?
Virtual Reality creates an entirely virtual world, while Augmented Reality overlays digital elements onto the real world. - Can Virtual Reality cause motion sickness?
Some users experience motion sickness due to the difference between their movement in the real world and the virtual world. - What is required to use Virtual Reality?
For most VR experiences, a VR headset and a compatible device, such as a gaming console or PC, are necessary. - How much does Virtual Reality cost?
VR headsets, depending on the model and features, cost from around $300 to over $1000. - What are the most popular uses of Virtual Reality?
Popular applications include gaming, education, healthcare, and real estate virtual tours.




